Introduction to Piraminds
The concept of piraminds is both fascinating and multifaceted, deeply rooted in history and culture. Often misconceived or considered merely structures, piraminds encompass much more in terms of architectural genius, societal significance, and philosophical depth. This article delves into the various aspects of piraminds, examining their historical background, architectural features, construction techniques, cultural importance, and their relevance today.
The Historical Background of Piraminds
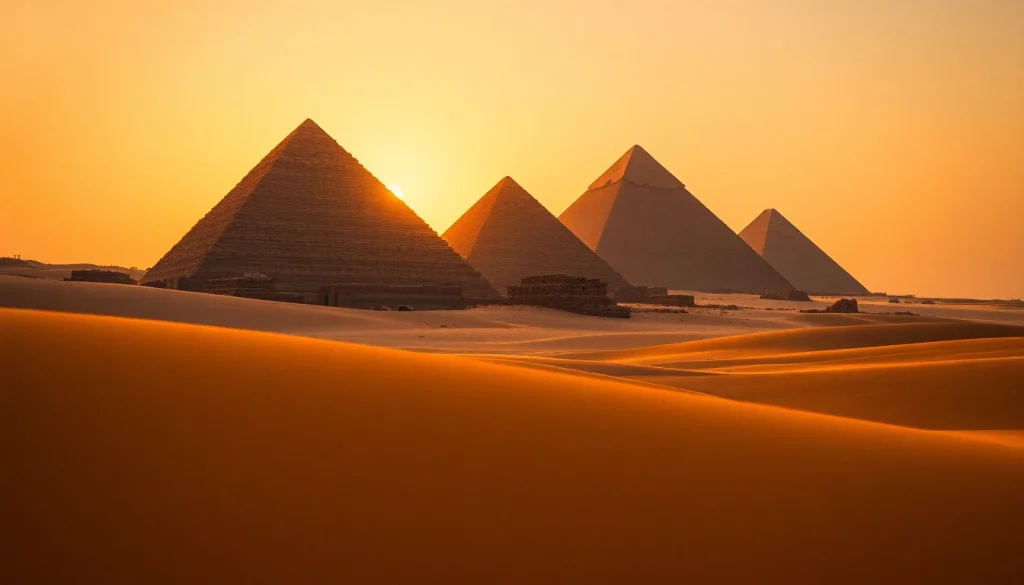
Piraminds have their origins in ancient civilizations, most prominently in Egypt, where they served as monumental tombs for pharaohs. The Great Pyramid of Giza, for instance, built during the Fourth Dynasty, exemplifies the pinnacle of piramid construction techniques. However, the concept of piraminds extends to several other cultures, including the Mesoamerican civilizations, which constructed their own versions with distinct purposes. Historical records indicate that piraminds were pivotal to societal structure, serving as religious symbols and royal burial chambers, highlighting the intersection of architecture and spirituality in ancient civilizations.
Types of Piraminds and Their Locations
Various types of piraminds exist worldwide, differing in structure and purpose. In Egypt, the most renowned are the pyramids of Giza, consisting of the Great Pyramid, Pyramid of Khafre, and Pyramid of Menkaure. Additionally, locations like Mesoamerica boast unique step pyramids, such as the Pyramid of Kukulcán in Chichén Itzá and the Pyramid of the Sun in Teotihuacan. Each piramid type reflects the architectural styles and cultural significances of their respective civilizations.
Architectural Features and Techniques of Piraminds
The architectural elements of piraminds are notably distinctive, often characterized by their triangular shape and massive stone blocks. The use of precise geometry in design is evident in structures like the Great Pyramid, which showcases advanced understanding in mathematics and astronomy. Techniques such as corbel arching and the innovative use of bevelled edges exhibit the ingenuity of ancient builders. Moreover, distinct features like the pyramidion—the pointed top of a piramid—often symbolized a connection to celestial bodies, representing a spiritual ascent for the deceased.
Construction and Engineering of Piraminds
Methods Used in Building Piraminds
Constructing a piramid was a monumental task that required advanced engineering techniques and significant human resources. Theories suggest that large blocks were transported using sledges over lubricated pathways, while ramps were likely employed to raise stone blocks to significant heights. Investigations into the methods of construction have unveiled various strategies including the use of levers and counterweights, which were critical in lifting heavy stones into place.
The Role of Labor in Piramid Construction
Labor played a crucial role in the construction of piraminds, representing a collective effort often involving thousands of workers. Contrary to the traditional belief that slaves built these structures, evidence suggests that skilled laborers were well-fed and housed, often mobilized from surrounding agricultural communities during the inundation season. This employment not only reflects the pyramids’ significance in society but also the advanced organizational capabilities of ancient governments.
Innovations Contributing to Piramid Engineering
Innovations in tools and methodologies significantly impacted piramid construction. The creation of copper tools allowed for more refined stone cutting and shaping. Additionally, significant advances in surveying techniques enabled builders to align structures with incredible precision with cardinal points, further showcasing their sophisticated understanding of astronomy and geography.
Cultural Significance of Piraminds
Piraminds in Ancient Egyptian Religion
In Ancient Egypt, piraminds symbolized the gateway for pharaohs to reach the afterlife. The structure itself was thought to facilitate this transition, aligning with their beliefs in the journey of the soul. Symbolism surrounding the piraminds often extended to the sun and its cycles, evident in the pyramid’s design and orientation towards the rising sun. This spiritual connotation cements the piramid’s role as more than a mere burial site but as a vital part of religious practice.
Symbolism and Spiritual Meaning of Piraminds
Piraminds encapsulate a deep spiritual meaning, often representing ascension and the connection between earth and the divine. The shape itself mimics the rays of the sun and is designed to reflect the journey of the soul toward immortality. This spiritual resonance extends beyond Egyptian culture, influencing other civilizations that integrated piramid-like structures into their religious frameworks, echoing similar themes of the afterlife and divine connection.
Piraminds in Modern Culture and Media
Modern culture continues to be fascinated with piraminds, appearing in numerous forms of media ranging from documentaries, literature, and art to video games and films. This ongoing fascination speaks to an enduring legacy, as new findings often spark renewed interest and research. The Great Pyramid, in particular, remains a symbol of mystery and human achievement, prompting exploration and conversation regarding its purpose and meaning throughout history.
Discovering Piraminds Today
Tourism Around Piraminds: An Overview
Piraminds attract millions of visitors each year, making them significant tourist destinations. In Egypt, the Pyramids of Giza remain at the forefront, offering tours that provide historical insights and showcase the intricacies of their architecture. Tourists can explore not only the piraminds themselves but also their surrounding complex structures, including temples and burial sites, enriching the visitor experience.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Conserving piraminds poses numerous challenges, primarily due to environmental degradation, tourism, and urban encroachments. Efforts are underway to restore and protect these ancient structures, involving careful monitoring of conditions and implementing preservation techniques. International cooperation is often crucial in these initiatives, emphasizing the global significance of preserving these historical sites.
Educational Programs Focusing on Piraminds
Educational efforts surrounding piraminds have expanded significantly, with programs aimed at increasing awareness and understanding of their history and cultural significance. Various institutions offer workshops, guided tours, and interactive experiences, helping to engage younger generations and promote further interest in archaeology and history.
Frequently Asked Questions about Piraminds
What are piraminds and their main purposes?
Piraminds are monumental structures primarily serving as tombs for ancient rulers. They symbolize power, the afterlife, and architectural prowess.
How are piraminds constructed?
Piraminds are constructed from massive stone blocks using advanced techniques for transportation and assembly, including ramps and sledges.
What historical significance do piraminds hold?
Piraminds represent the political and religious ideologies of ancient civilizations, reflecting their values, beliefs, and engineering capabilities.
What is the cultural symbolism of piraminds?
Piraminds symbolize a connection between the earth and the divine, embodying themes of ascension, immortality, and the afterlife.
How can one visit piraminds today?
Many piraminds are accessible to the public, with organized tours available at major sites like the Pyramids of Giza, providing insights into their history and architecture.